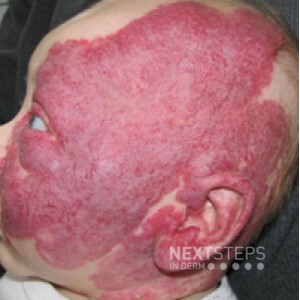
The correct answer is E. Coarctation of the aorta.
This patient has a segmental infantile hemangioma on the face and should be evaluated for PHACES syndrome: posterior fossa malformations, hemangiomas, arterial anomalies, cardiac defects and coarctation of the aorta (Choice 5), eye anomalies, sternal defects and supraumbilical raphe. Work-up includes MRI/MRA of the head and neck, referral to a cardiologist, and referral to a pediatric ophthalmologist.
Cleft palate (Choice A), diaphragmatic hernia (Choice B), hypospadias (Choice C), imperforate anus (Choice D) are not associated with PHACES syndrome.
References: Bolognia, Jean., Jorizzo, Joseph L.Schaffer, Julie V. (Eds.) (2012) Dermatology /[Philadelphia] : Elsevier Saunders
