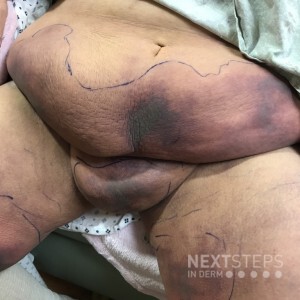
The correct answer is C. Calciphylaxis.
An obese patient with dusky, retiform and stellate necrotic plaques predominantly on the fatty areas of the body is most consistent with calciphylaxis. The differential diagnosis includes warfarin necrosis. Oxalate or cholesterol emboli can in rare cases resemble calciphylaxis, but tend to affect distal extremities as opposed to fatty, central areas.
Mixed cryoglobulinemia is a vasculitis, which manifests with palpable purpura as opposed to retiform or stellate purpura and necrosis. Cold panniculitis is a subcutaneous disorder which manifests with painful pink-red to violaceous plaques – this condition is seen most often in newborns, but can affect adults and is usually seen on the outer thighs of adults (equestrian panniculitis). Homozygous deficiency or severe dysfunction of either protein C or protein S leads to neonatal purpura fulminans within a few hours to 5 days after birth, and it is fatal unless treated. Sneddon syndrome is a vascular disorder which manifests with widespread livedo reticularis or racemosa with CNS problems (stroke, TIA, seizures). There is no retiform purpura or necrosis apparent.
Reference: Bolognia, Jean., Jorizzo, Joseph L.Schaffer, Julie V. (Eds.) (2012) Dermatology /[Philadelphia] : Elsevier Saunders
