The correct answer is B. Anterior ethmoidal.
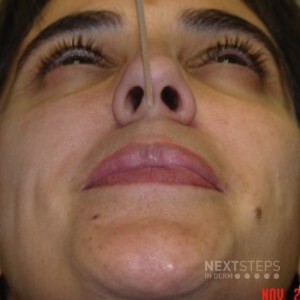
The external nasal nerve innervates the columella and nasal tip. It is a branch of the anterior ethmoidal nerve, which provides branches of V1. The infratrochlear is also a branch of V1 but it supplies the nasal root and medial canthus. The infraorbital and zygomaticotemporal are branches of V2. The buccal is a branch of V3.
Most of the sensory innervation of the nasal cavity is derived from two sources: the sphenopalatine ganglion and the anterior ethmoidal nerve. The sphenopalatine ganglion (pterygopalatine, nasal, or Meckel’s ganglion) is a parasympathetic ganglion that is located in the pterygopalatine fossa, posterior to the middle turbinate. Its sensory root is derived from sphenopalatine branches of the maxillary nerve, cranial nerve (CN) V2. As they pass through the sphenopalatine ganglion, these sensory branches form the greater and lesser palatine nerves, which provide sensory innervation to the nasal cavity as well as the roof of the mouth, soft palate, and tonsils. The anterior ethmoidal nerve is one of the sensory branches of the ciliary ganglion, which is located within the orbital cavity and inaccessible to nerve blocks. It provides sensory innervation to the anterior portion of the nasal cavity.
References: Chotiyanonta JS, Dinovo KM, McCulloch PF. Bilateral sectioning of the anterior ethmoidal nerves does not eliminate the diving response in voluntarily diving rats. Physiol Rep. 2013 Nov;1(6):e00141. doi: 10.1002/phy2.141. Epub 2013 Nov 7. PMID: 24400143; PMCID: PMC3871456.
