The correct answer is D. Interleukin-31.
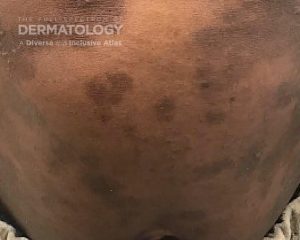
Approximately 10% of cases of mastocytosis present as a solitary lesion, otherwise known as a mastocytoma. Typically, they present in childhood on the trunk or wrist and usually are self-limited and spontaneously resolve. Histologically, the epidermis overlying the mast cell proliferation is often hyperpigmented. Within the dermis, there are increased numbers of “fried egg” mast cells. Often, the mast cells are primarily located in the upper dermis, where they fill and expand the dermal papillae. Frequently admixed among the mast cells, there are increased numbers of eosinophils. Mast cells contain a variety of substances, but a major one is histamine.
Antibodies are usually found in lymphocytes, major basic protein is found in eosinophils, melanin can be found in keratinocytes or melanocytes, and myeloperoxidases can be found in neutrophils. None of these are the main cell type implicated in this condition.
References:
Tanaka S, Furuta K. Roles of IgE and Histamine in Mast Cell Maturation. Cells. 2021;10(8):2170. Published 2021 Aug 23. doi:10.3390/cells10082170
