The correct answer is B. 7-21 days.
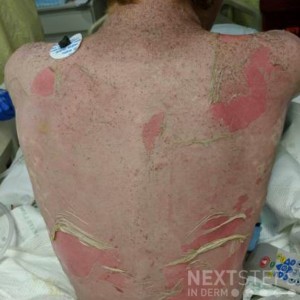
Extensive oral erosion coupled with widespread epidermal detachment is highly concerning for Stevens-Johnson syndrome/Toxic epidermal necrolysis (SJS/TEN), which is a severe cutaneous adverse reaction that is almost always drug-related. The most common offending drugs include: antibiotics (especially sulfonamides and penicillins), allopurinol, anticonvulsants (often lamotrigine, carbamazepine, or phenytoin), barbiturates, NSAIDs, and anti-retrovirals. For SJS/TEN, the typical onset of eruption after drug ingestion is 7-21 days (although it can be up to 60 days for anticonvulsants). Hours to 2 days is typical for acute generalized exathematous pustulosis (AGEP). Drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) syndrome usually occurs 21-56 days after medication exposure. Lichenoid drug eruptions and drug-induced pemphigus may occur several weeks or months after drug initiation.
