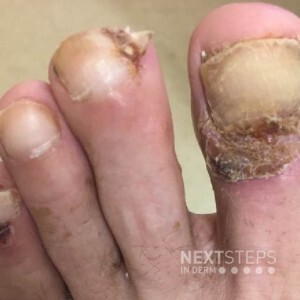
The correct answer is A. Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) inhibitor.
This photo depicts paronychia. Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) inhibitors, such as Cetuximab and panitumumab, cause a variety of cutaneous adverse reactions including paronychia, papulopustular (acneiform) eruptions, photosensitivity, skin fragility, and hair changes.
TNFa inhibitors (etanercept, adalimumab, infliximab) may be associated with injection site reactions and paradoxical psoriasiform eruptions. Smoothened inhibitors (vismodegib and sonidegib) are associated with muscle spasm, alopecia, and dysgeusia. BRAF inhibitors (vemurafenib, dabrafenib) are associated with maculopapular eruptions, photosensitivity, seborrheic dermatitis-like eruptions, keratosis pilaris-like eruptions, panniculitis, and squamoproliferative growths. PD-1 inhibitors (Pembrolizumab, Nivolumab) are associated with maculopapular eruptions, alopecia, oral mucositis, pruritus, lichenoid eruptions, and vitiligo.
Reference: Macdonal JB, et al. Cutaneous adverse effects of targeted therapies Part I: Inhibitors of the cellular membrane. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015;72:203-18.
