The correct answer is C. Tram-track calcifications of the temporal and occipital cortex.
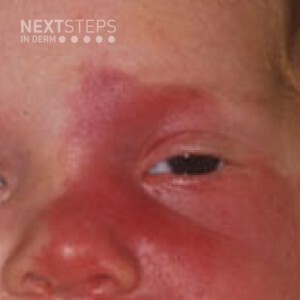
Sturge-Weber syndrome is a sporadic disorder characterized by a facial capillary malformation in a trigeminal nerve distribution. Patients with Sturge-Weber may have cerebral atrophy, ipsilateral vascular malformations of the leptomeninges, seizures, and glaucoma. The classic radiologic finding is tram-track calcifications of the temporal and occipital cortex.
Dural calcifications are seen in Papillon-Lefevre syndrome. Calcification of the falx cerebri is seen in Gorlin’s Syndrome. Osteopatha Striata is seen in Goltz syndrome. Osteopoikilosis is seen in Buschke Ollendorf syndrome.
Reference:
Thomas-Sohl KA, Vaslow DF, Maria BL. Sturge-Weber syndrome: a review. Pediatr Neurol. 2004 May;30(5):303-10. PMID: 15165630
