JDD April 2024 Issue Highlights
215362153621536 Introducing the April 2024 Editorial Highlights from the Journal of Drugs in Dermatology! This month's issue is packed with groundbreaking research and insights into dermatologic treatments and practices. From original articles exploring innovative therapies for conditions like photoaging and acne vulgaris to case reports shedding light on rare dermatologic phenomena, this issue offers a comprehen …
Introducing the April 2024 Editorial Highlights from the Journal of Drugs in Dermatology! This month's issue is packed with groundbreaking research and insights into dermatologic treatments and practices. From original articles exploring innovative therapies for conditions like photoaging and acne vulgaris to case reports shedding light on rare dermatologic phenomena, this issue offers a comprehen …
 Introducing the April 2024 Editorial Highlights from the Journal of Drugs in Dermatology! This month's issue is packed with groundbreaking research and insights into dermatologic treatments and practices. From original articles exploring innovative therapies for conditions like photoaging and acne vulgaris to case reports shedding light on rare dermatologic phenomena, this issue offers a comprehen …
Introducing the April 2024 Editorial Highlights from the Journal of Drugs in Dermatology! This month's issue is packed with groundbreaking research and insights into dermatologic treatments and practices. From original articles exploring innovative therapies for conditions like photoaging and acne vulgaris to case reports shedding light on rare dermatologic phenomena, this issue offers a comprehen … 

 Intravenous immune globulin (IVIG) is a concentrate of pooled immunoglobulins derived from plasma donors. Its unique mechanism of action expands the utility of the medication to a variety of conditions. We continue our series, Therapeutic Cheat Sheet, with a closer look at IVIG, which is FDA-approved for the treatment of dermatologic conditions including dermatomyositis, Kawasaki disease, ITP, and …
Intravenous immune globulin (IVIG) is a concentrate of pooled immunoglobulins derived from plasma donors. Its unique mechanism of action expands the utility of the medication to a variety of conditions. We continue our series, Therapeutic Cheat Sheet, with a closer look at IVIG, which is FDA-approved for the treatment of dermatologic conditions including dermatomyositis, Kawasaki disease, ITP, and …  At ODAC 2023, we had the opportunity to learn about the latest in treatments for blistering diseases from Dr. Karl Saardi, Associate Professor and Director of Inpatient Dermatology at George Washington University. We focused on the pemphigus and pemphigoid group of diseases, which we will review and summarize here.
Pemphigus
The pemphigus group of diseases is characterized by intraepidermal auto …
At ODAC 2023, we had the opportunity to learn about the latest in treatments for blistering diseases from Dr. Karl Saardi, Associate Professor and Director of Inpatient Dermatology at George Washington University. We focused on the pemphigus and pemphigoid group of diseases, which we will review and summarize here.
Pemphigus
The pemphigus group of diseases is characterized by intraepidermal auto … 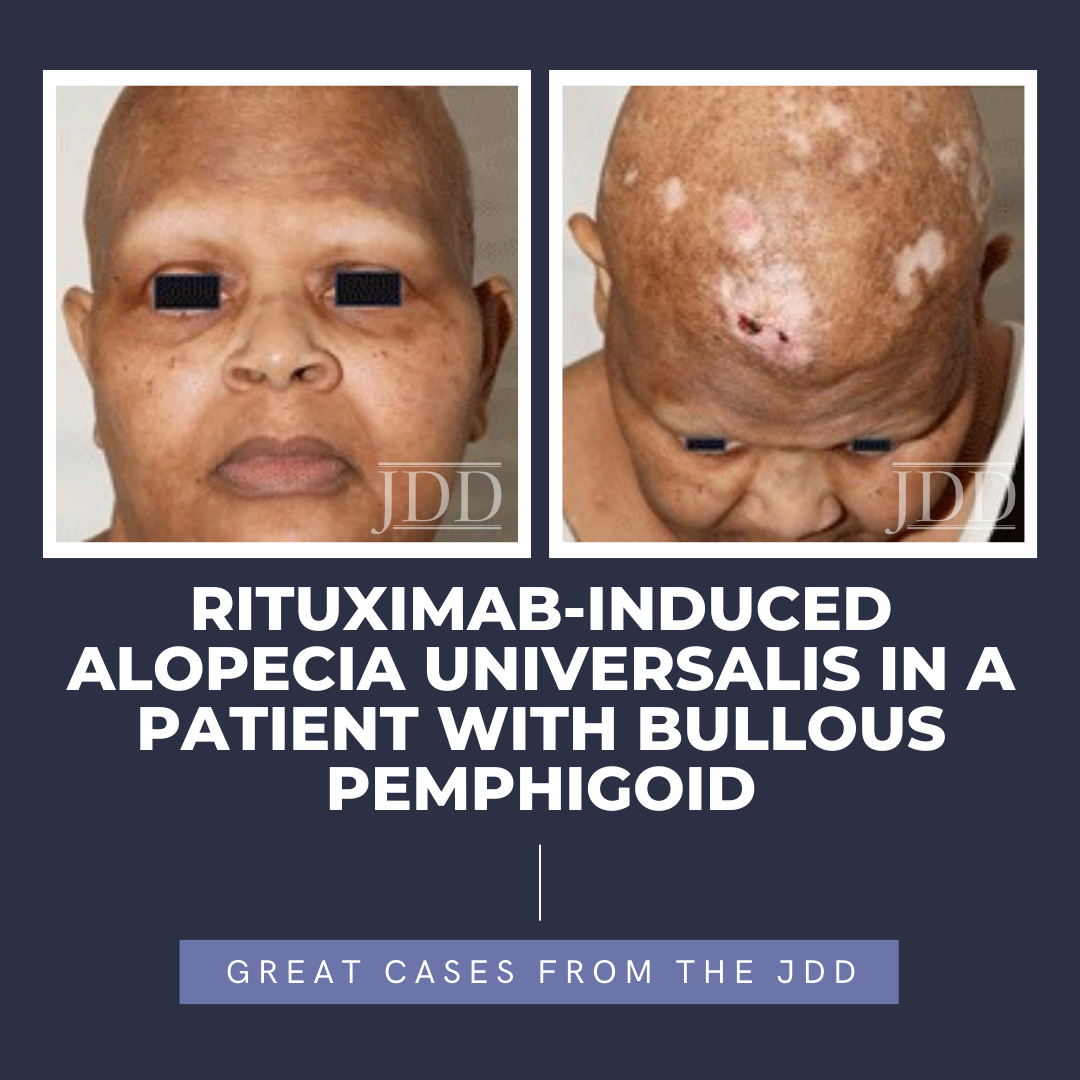 Alopecia areata is a CD8+ T-lymphocyte driven autoimmune disorder leading to reversible hair loss. While most commonly presenting as isolated well-demarcated non-cicatricial alopecic patches on the scalp, subtypes of alopecia areata include alopecia totalis with loss of all scalp hair and alopecia universalis with complete loss of all body hair. Although primarily an idiopathic condition, several …
Alopecia areata is a CD8+ T-lymphocyte driven autoimmune disorder leading to reversible hair loss. While most commonly presenting as isolated well-demarcated non-cicatricial alopecic patches on the scalp, subtypes of alopecia areata include alopecia totalis with loss of all scalp hair and alopecia universalis with complete loss of all body hair. Although primarily an idiopathic condition, several … 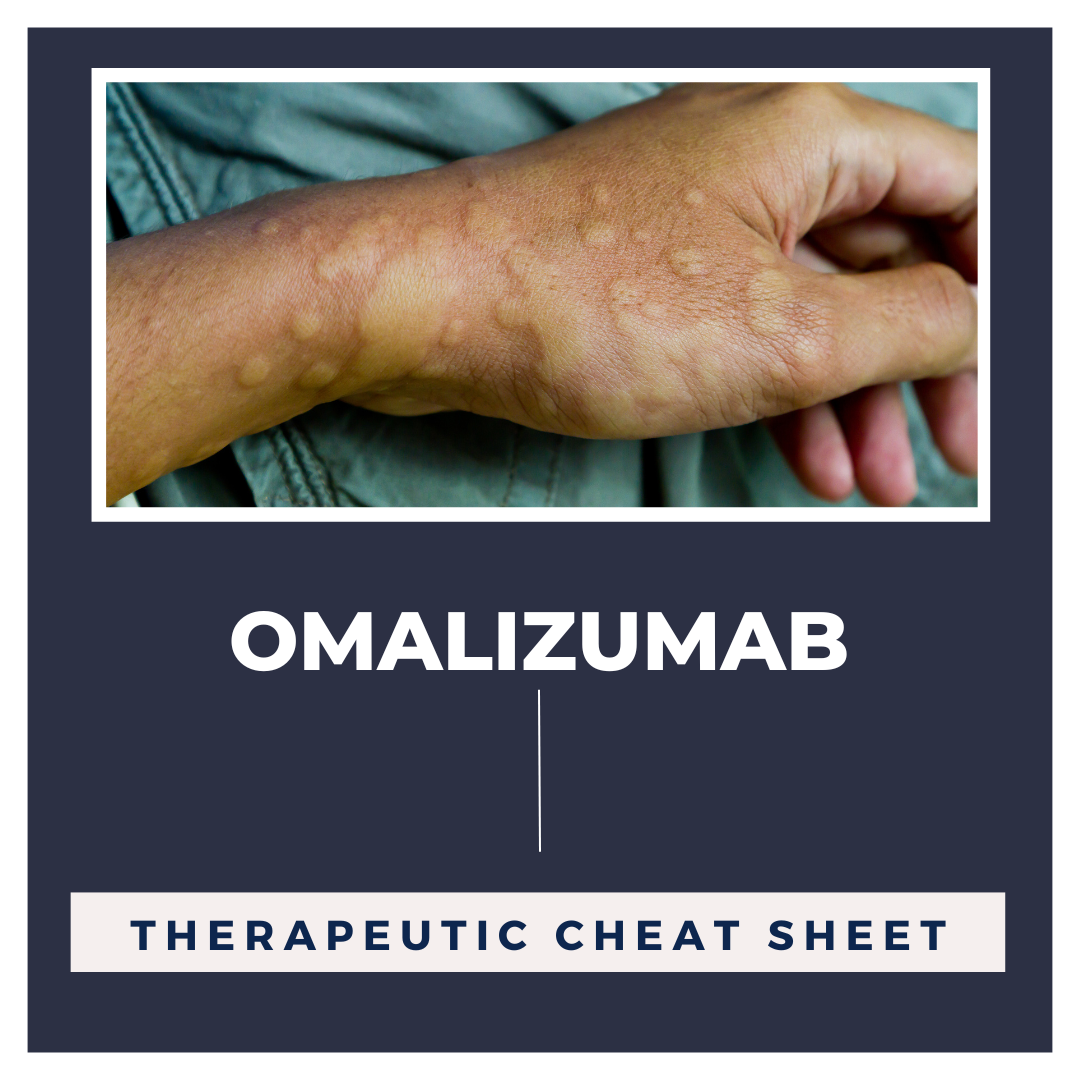 Chronic idiopathic urticaria is urticaria for greater than 6 weeks without an identifiable trigger. Cases relapse in 20% of patients for more than 5 years and be difficult to manage; however, omalizumab is a recently approved option for treatment of chronic idiopathic urticaria showing beneficial outcomes.1 Omalizumab is an injectable monoclonal antibody that has been FDA approved not just for chr …
Chronic idiopathic urticaria is urticaria for greater than 6 weeks without an identifiable trigger. Cases relapse in 20% of patients for more than 5 years and be difficult to manage; however, omalizumab is a recently approved option for treatment of chronic idiopathic urticaria showing beneficial outcomes.1 Omalizumab is an injectable monoclonal antibody that has been FDA approved not just for chr …